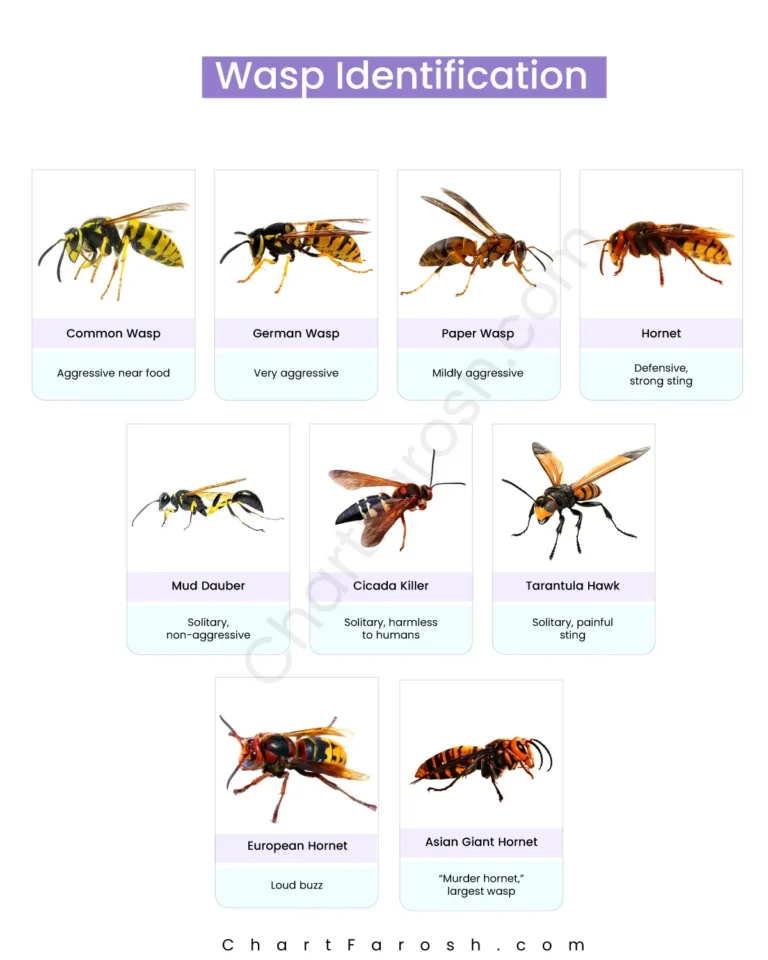
Flying Insect Identification Chart
Flying insects are often seen as pests, but they can be more than just a nuisance. They can give clues about your surroundings, like fruit flies hinting at overripe produce or drain flies showing damp conditions. By noticing these insects, you might uncover hidden issues in your environment.
Learning to identify different flying insects can help you address these problems early. The details below will help you recognize and understand the various types of flying insects you might find around your home.

Table of Contents
Flying Insect Identification Chart
Flying insects often go unnoticed until they become a nuisance, but their presence can indicate much more than a simple pest problem. Many flying insects are linked to specific environmental conditions or human activities, offering clues to underlying issues in your surroundings.
For example, the sudden appearance of certain species could point to excess moisture, decaying organic matter, or even improperly stored food. Recognizing these subtle signals can help you address potential problems before they escalate.
The table below provides detailed identification markers for various flying insects, helping you better understand and manage their presence in your environment.
| Insect Type | Appearance | Behavior | Habitat |
| Housefly | Grayish body with four dark stripes on the back | Feeds on food waste and decaying matter | Kitchens, garbage, decaying organic matter |
| Fruit Fly | Small, reddish-brown body, large red eyes | Attracted to fermenting fruit and vegetables | Kitchens, fruit bowls, compost bins |
| Drain Fly | Small, fuzzy, grayish-brown with moth-like wings | Breeds in damp, organic matter in drains | Drains, sinks, damp areas |
| Moth | Various colors, often with drab or patterned wings | Attracted to light, feeds on clothing or food | Closets, attics, pantry areas |
| Fungus Gnat | Tiny, black with delicate wings, resembling mosquitoes | Feeds on decaying organic matter in soil | Potted plants, soil, damp areas |
| Cockroach (Flying Species) | Brown to black, with large wings | Typically hidden but can fly, especially when disturbed | Kitchens, bathrooms, dark corners |
| Wasps | With a tougher build, it is black and yellow | Often aggressive, they stay near food and build nests inside homes | Pantries, kitchens, wall cavities |
| Silverfish (Flying Species) | Silver-gray, with long antennae and bristly body | Fast-moving, prefers dark, damp areas | Basements, bathrooms, storage areas |
| Beetle (Flying Species) | Varied colors and sizes, often with hard wing cases | Diverse diets, can be pests or beneficial | Kitchens, food storage areas, gardens |
| Yellow Jacket | Black and yellow with a robust body | Aggressive, can nest indoors, especially near food | Pantries, wall cavities, near food |
| Carpet Beetle | Small, round, often with patterned or mottled wings | Feeds on natural fibers, can damage carpets and clothing | Carpets, clothing, storage areas |
| Indian Meal Moth | Brownish-gray with reddish-brown markings | Feeds on stored grains and cereals | Pantries, grain storage, dried food |
| Clothes Moth | Small, golden or tan with tiny wings | Feeds on natural fibers in clothing and textiles | Closets, wardrobes, storage areas |
| Gnats | Tiny, black or brown, with delicate wings | Often seen in swarms, attracted to decaying matter | Damp areas, overwatered plants, drains |
| Booklice | Tiny, light-colored with translucent wings | Feeds on mold and fungi, found in damp environments | Books, paper products, damp areas |
| Asian Lady Beetle | Small, often red with black spots | Beneficial for gardens but can invade homes in fall | Near windows, warm areas in autumn |
| Sphinx Moth | Big in size, tough wings, and usually has eye-catching design | Hover feeds on nectar, usually at night | Gardens, near flowering plants, nighttime activity |
Types of Flying Insects
Flying insects are not just a single group of creatures, they encompass a wide range of species, each playing a distinct role in the ecosystem. Understanding these roles can help us appreciate the importance of these insects and their impact on the environment.
A flying insect identification chart with pictures can be a valuable tool in distinguishing these various species by their ecological functions. It offers a clearer picture of their contributions and behaviors.
Below, the types of flying insects are categorized by their roles:
Pollinators
Insects like bees, butterflies, and certain types of beetles are crucial for the pollination of plants. They carry pollen to other flowers, helping fruits, seeds, and vegetables to grow. Without these pollinators, many of the foods we rely on would be in short supply.
Decomposers
Among flying insects, beetles and flies stand out as decomposers. They break down decaying matter and recycle it into the soil as nutrients. It helps maintain soil fertility and ensures plants can grow well.
Pests
Some flying insects, such as mosquitoes and houseflies, are often considered pests due to their tendencies to bite, spread diseases, or contaminate food sources. These insects can have a direct impact on human health and well-being, making their management an important task.
Predators
Dragonflies, certain species of wasps, and ladybugs fall into the category of predators. These insects play a vital role in controlling the populations of other insects, particularly pests, by preying on them. This natural form of pest control is essential for maintaining ecological balance.
Most Common Flying Insect
In everyday environments, certain flying insects are more likely to be encountered, often becoming part of our daily routines in homes, gardens, and urban areas. Recognizing these common insects quickly can help in managing their presence and minimizing any potential issues they may cause.
Here are some of the most frequently encountered flying insects and practical tips for dealing with them:
Houseflies
Often found buzzing around kitchens and garbage bins, houseflies are attracted to food waste and decaying organic matter. Keeping food sealed, cleaning up spills immediately, and regularly disposing of trash can help reduce their numbers indoors.
Mosquitoes
These tiny, blood-feeding insects are not only a nuisance but can also transmit diseases. They’re most active around dawn and dusk, frequently near calm water where they lay their eggs. Eliminating standing water around your home and using insect repellent can help keep them at bay.
Fruit Flies
These small insects are often seen hovering around ripe or fermenting fruits and vegetables. To manage fruit flies, keep produce covered, store it in the refrigerator, and clean up any spills or crumbs that could attract them.
Moths
Moths are attracted to light and can often be found fluttering around lamps and light fixtures. They can also be problematic in closets where they may feed on natural fibers. Using mothballs or cedar blocks in storage areas and keeping outdoor lights off when not needed can help minimize their presence.
Bees and Wasps
While bees are essential pollinators, their presence near homes can be concerning, especially for those allergic to stings. In comparison, wasps tend to display higher levels of aggression.
To coexist safely, avoid swatting at them, keep sweet foods and drinks covered when outdoors, and consider professional removal if a nest is found close to living areas.
Black Flying Insect Identification
Identifying black flying insects can be particularly challenging due to the similar appearance many of them share. Their dark coloration often masks subtle differences, making it difficult to distinguish one species from another at a glance.
However, by paying close attention to specific features such as wing shape, size, and unique behaviors, you can more accurately identify these insects.
Below are key aspects to consider when differentiating between common black flying insects:
Wing Shape and Position
Some black flying insects, like the common housefly, have broad wings that lay flat over their backs when at rest. In contrast, the black wasp’s wings are narrower and typically fold along their bodies. Observing how the wings are positioned when the insect is at rest can be a useful identification clue.
Size Variations
The size of black flying insects can vary greatly, providing a useful point of comparison. For example, the black carpenter bee is significantly larger and more robust than a tiny fungus gnat. Measuring or estimating size can help narrow down the possibilities.
Behavioral Traits
Behavior is another key identifier. For instance, black flies are often found near water sources and are known for their painful bites. Meanwhile, black ants with wings are frequently seen swarming in large numbers, usually during their mating season. Recognizing these behaviors can be essential for proper identification.
Antennae and Legs
The shape and length of antennae and legs can also differ among species. For example, black beetles with wings may have prominent, club-shaped antennae, whereas black moths often have feathery antennae. Similarly, the length of legs in relation to the body can help in distinguishing between species.
Brown Flying Insect
Brown flying insects are often associated with environments rich in organic material, where they play various roles in the ecosystem. These insects can range from harmless pollinators to potential pests, and identifying them accurately can help manage their impact on your surroundings.
The subtle differences in their appearance and behavior offer clues to their identification and role in the environment.
Body Texture and Shape
Many brown flying insects, such as moths, have soft, fuzzy bodies, while others like beetles have hard, shiny exoskeletons. Observing the texture and shape of the insect’s body can provide insight into its species and habits.
Wing Patterns
Wing patterns are often a distinguishing feature among brown flying insects. For example, the brown lacewing has delicate, net-like wings, while brown moths typically have solid or subtly patterned wings. These patterns can help differentiate between similar-looking insects.
Behavioral Habits
Brown flying insects often exhibit specific behaviors linked to their environment. For instance, fungus gnats, which are small and often mistaken for other brown insects, are attracted to damp soil and can be seen hovering around potted plants.
On the other hand, brown stink bugs are often found on fruits and vegetables, releasing a distinctive odor when disturbed.
Preferred Habitats
The preferred habitat of a brown flying insect can also aid in identification. Some are drawn to indoor environments, like the brown house fly, while others, like the brown beetle, are more commonly found in gardens or wooded areas. Recognizing where these insects are most likely to be found can help in narrowing down their identity.
Also read: Insects Edd id Guide
Conclusion
Dealing with flying insects doesn’t have to be overwhelming. With a bit of knowledge, you can easily manage them in your home or garden. By recognizing what to look for, you’ll feel more confident in handling any situation.
Whether you’re aiming to keep pests at bay or just curious about the insects around you, a little understanding goes a long way. Taking the time to learn about these creatures not only helps you deal with them but also gives you a new perspective on the important roles they play.